-
Civics
24-
Power Sharing 41 minLecture1.1
-
Chapter Notes – Power SharingLecture1.2
-
NCERT Solutions – Power SharingLecture1.3
-
Federalism 01 hourLecture1.4
-
Chapter Notes – FederalismLecture1.5
-
NCERT Solutions – FederalismLecture1.6
-
Gender Caste 01 hour 04 minLecture1.7
-
Chapter Notes – Gender CasteLecture1.8
-
NCERT Solutions – Gender CasteLecture1.9
-
Popular Struggles 01 hour 18 minLecture1.10
-
Chapter Notes – Popular StrugglesLecture1.11
-
NCERT Solutions – Popular StrugglesLecture1.12
-
Political Parties 55 minLecture1.13
-
Chapter Notes – Political PartiesLecture1.14
-
NCERT Solutions – Political PartiesLecture1.15
-
Democracy and Diversity 49 minLecture1.16
-
Chapter Notes – Democracy and DiversityLecture1.17
-
NCERT Solutions – Democracy and DiversityLecture1.18
-
Outcome of Democracy 41 minLecture1.19
-
Chapter Notes – Outcome of DemocracyLecture1.20
-
NCERT Solutions – Outcome of DemocracyLecture1.21
-
Challenges to Democracy 53 minLecture1.22
-
Chapter Notes – Challenges to DemocracyLecture1.23
-
NCERT Solutions – Challenges to DemocracyLecture1.24
-
-
Economics
37-
Development 1 – Introduction 57 minLecture2.1
-
Development 2 – Levels of Devplopment-Individual 23 minLecture2.2
-
Development 3 – Levels of Development-National 32 minLecture2.3
-
Development 4 – Development in Country, Type of Resources 10 minLecture2.4
-
Development 5 – Levels of Devplopment-Individual_English 23 minLecture2.5
-
Development 6 – Levels of Devplopment-National_English 32 minLecture2.6
-
Development 7 – Development in Country, Type of Resources_English 10 minLecture2.7
-
Chapter Notes – DevelopmentLecture2.8
-
NCERT Solutions – DevelopmentLecture2.9
-
Money and Credit 1 38 minLecture2.10
-
Money and Credit 2 23 minLecture2.11
-
Money and Credit 3 23 minLecture2.12
-
Chapter Notes – Money and CreditLecture2.13
-
NCERT Solutions – Money and CreditLecture2.14
-
Sectors of Indian Economy 1- Introduction 44 minLecture2.15
-
Sectors of Indian Economy 2 – Some Important Terms, Activity in Primary and Secondary Sector, Teritary Sector 01 hour 06 minLecture2.16
-
Sectors of Indian Economy 3 – Devision of Sectors as Organised and Unorganised 21 minLecture2.17
-
Sectors of Indian Economy 4 – Some Important Terms, Activity in Primary and Secondary Sector, Teritary Sector_English 01 hour 06 minLecture2.18
-
Sectors of Indian Economy 5 – Devision of Sectors as Organised and Unorganised_English 21 minLecture2.19
-
Chapter Notes – Sectors of Indian EconomyLecture2.20
-
NCERT Solutions – Sectors of Indian EconomyLecture2.21
-
Globalization of the Indian Economy 1- Globalization of the Indian Economy 01 hour 39 minLecture2.22
-
Globalization of the Indian Economy 2- Economics Polices, Captalist Economy, Socialist Economy 34 minLecture2.23
-
Globalization of the Indian Economy 3- Production Activity, Interlinking Production Across Countries 23 minLecture2.24
-
Globalization of the Indian Economy 4 – Forien Trade and Integration of Market, 20 minLecture2.25
-
Globalization of the Indian Economy 5 – Factors That Have Enabled Globalisation, Steps to Attract Foreign Investment 24 minLecture2.26
-
Globalization of the Indian Economy 6 – Economics Polices, Captalist Economy, Socialist Economy_English 34 minLecture2.27
-
Globalization of the Indian Economy 7 – Production Activity, Interlinking Production Across Countries_English 23 minLecture2.28
-
Globalization of the Indian Economy 8 – Forien Trade and Integration of Market_English 20 minLecture2.29
-
Globalization of the Indian Economy 9 – Factors That Have Enabled Globalisation, Steps to Attract Foreign Investment_English 25 minLecture2.30
-
Chapter Notes – Globalization of the Indian EconomyLecture2.31
-
NCERT Solutions – Globalization of the Indian EconomyLecture2.32
-
Consumer Rights 1 – Introduction 45 minLecture2.33
-
Consumer Rights 2 – Goods and Services, Unfair Trade Practices 31 minLecture2.34
-
Consumer Rights 3 – Different Types of Rights 42 minLecture2.35
-
Chapter Notes – Consumer RightsLecture2.36
-
NCERT Solutions – Consumer RightsLecture2.37
-
-
Geography
28-
Resources and Development 1 53 minLecture3.1
-
Resources and Development 2 44 minLecture3.2
-
Chapter Notes – Resources and DevelopmentLecture3.3
-
NCERT Solutions – Resources and DevelopmentLecture3.4
-
Forest and Wildlife 48 minLecture3.5
-
Chapter Notes – Forest and WildlifeLecture3.6
-
NCERT Solutions – Forest and WildlifeLecture3.7
-
Water Resources 1 12 minLecture3.8
-
Water Resources 2 49 minLecture3.9
-
Chapter Notes – Water ResourcesLecture3.10
-
Agriculture 1 01 hour 06 minLecture3.11
-
Agriculture 2 10 minLecture3.12
-
Chapter Notes – AgricultureLecture3.13
-
Minerals and Energy Resources 1 45 minLecture3.14
-
Minerals and Energy Resources 2 58 minLecture3.15
-
Minerals and Energy Resources 3 49 minLecture3.16
-
Minerals and Energy Resources 4 38 minLecture3.17
-
Chapter Notes – Minerals and Energy ResourcesLecture3.18
-
Lifeline of National Economy 1 37 minLecture3.19
-
Lifeline of National Economy 2 26 minLecture3.20
-
Lifeline of National Economy 3 40 minLecture3.21
-
Lifeline of National Economy 4 29 minLecture3.22
-
Lifeline of National Economy 5 33 minLecture3.23
-
Chapter Notes – Lifeline of National EconomyLecture3.24
-
NCERT Solutions – Lifeline of National EconomyLecture3.25
-
Manufacturing Industries 02 hourLecture3.26
-
Chapter Notes – Manufacturing IndustriesLecture3.27
-
NCERT Solutions – Manufacturing IndustriesLecture3.28
-
-
History
28-
The Age of Industrialization 01 hourLecture4.1
-
Chapter Notes – The Age of IndustrializationLecture4.2
-
NCERT Solutions – The Age of IndustrializationLecture4.3
-
Rise of Nationalism in Europe 01 hourLecture4.4
-
Chapter Notes – Rise of Nationalism in EuropeLecture4.5
-
NCERT Solutions – Rise of Nationalism in EuropeLecture4.6
-
The Making of a Global World 01 hourLecture4.7
-
Chapter Notes – The Making of a Global WorldLecture4.8
-
NCERT Solutions – The Making of a Global WorldLecture4.9
-
Globalization – Part 1 01 hourLecture4.10
-
Globalization – Part 2 42 minLecture4.11
-
Work Life Leisure 01 hourLecture4.12
-
The Nationalist Movement in Indo-China 1 35 minLecture4.13
-
The Nationalist Movement in Indo-China 2 01 hourLecture4.14
-
The Nationalist Movement in Indo-China 3 59 minLecture4.15
-
Nationalist Movement in India 1 23 minLecture4.16
-
Nationalist Movement in India 2 51 minLecture4.17
-
Nationalist Movement in India 3 01 hourLecture4.18
-
Nationalist Movement in India 4 20 minLecture4.19
-
Chapter Notes – Nationalism in IndiaLecture4.20
-
NCERT Solutions – Nationalism in IndiaLecture4.21
-
Novels Society and History 1 55 minLecture4.22
-
Novels Society and History 2 32 minLecture4.23
-
Novels Society and History 3 50 minLecture4.24
-
Print Culture and Modern World 1 01 hourLecture4.25
-
Print Culture and Modern World 2 47 minLecture4.26
-
Chapter Notes – Print Culture and Modern WorldLecture4.27
-
NCERT Solutions – Print Culture and Modern WorldLecture4.28
-
Chapter Notes – Money and Credit
-
- Overview
- Money as a medium of exchange
- Modern form of money
- Loan activities of bank
- Two different credit situation
- Terms of credit
- Formal sector credit in India
- Self-help groups for the poor
Overview
(i) Money is a fascinating subject.
(ii) Modern forms of money are linked to the banking system.
(iii) Functions of money.
(iv) Creation of money.
(v) Credit is a crucial element in economic life.
(vi) Other crucial issue of credit is its availability to all.
• Money is an item which is used as a medium of exchange. In modern economy, money is work as an intermediary. It is used as a medium of exchange for goods and services. It is also used for payment of debts.
Modern form of money
(i) Currency
• Modern forms of money include currency — paper notes and coins. The modern coins are not made with the precious metals like gold, silver. The real values of the modern coins are less than its face value. Currency notes are also used as a medium of exchange in modern economy. The currency notes are made with paper. The real values of the currency notes are less than its face value.
• The currency is authorized by the government of the country. So, it is used as a medium of exchange and accepted by the others. In India, Reserve bank of India has authority to issue currency notes on behalf of the central government. In India, no individual can legally refuse to accept the rupees issued by the Reserve bank of India.
(ii) Deposits with Banks
• Deposits with Banks are also a form of money. A person can deposit in the bank by opening an account on his/her name. People need only some money at a point of time. So, people can deposit extra money and earn extra money, which is given on money already depositing in bank.
Loan activities of bank
• Bank work as mediator between the depositors and the borrowers. People deposit their money in bank and get some rate of interest as extra income. Banks hold only some percentage of their deposit in bank.
• A major portion of the deposited money is provided to those people who are needy of money for economic activities.In this case, money is provided as a loan with a higher rate of interest. The difference between interest on borrowing money and the interest of deposited money is the income for the bank.
Two different credit situations
• Credit is an agreement in which is created when a person gives money and goods to the needy person with the promise of to repay that with some rate of interest.
• There are two types of credit situation
(i) In the first situation, a person borrows money for production activities with the promise to repay the loan at the end of the year when production work will be completed. And at the end of the year, he/she makes a good profit from production activities and he/she is able to pay the amount of loan. Therefore, that person becomes better off than before.
(ii) In the second situation, a person borrows money for production activities with the promise to repay the loan at the end of the year when production work will be completed. And at the end of the year he/she unable to repay the loan due to loss in production. For this term, he/she come under the situation of debt trap. Therefore, that person becomes worse off than before.
Terms of credit
• Collateral is an asset of the borrowers which is given to the lenders as security for the specified period. A lender can use the assets which are held by him as security until the amount of loan is repaid. The lender has right to sell the assets or collateral when the borrower fails to repay the amount of loan in a specified period.
Formal sector credit in India
• There are two types of sources of credit in an economy.
(ii) Informal sector
• Formal sector
In the formal sector, loans from banks and cooperatives are included.
• Informal sector
In the Informal sector, loans from moneylenders, traders, employers, relatives and friends are included.
• As we know that major portion of the deposited money is provided to those people who are needy of money for economic activities. In India Reserve bank of India is supervised the functioning of loan activities in formal sectors. In India, the rate of interest in informal sector is greater than the rate of interest in formal sector. Rate of interest in formal sector is supervised by the legal authorities.
• In the Informal sector, the rate of interest is supervised by moneylenders, traders, employers who are provided money. The rate of interest is varying from person to person. There is no organization for supervising loan in informal sector. Lenders can use any method to get back their money from the borrowers. Sometimes, the incomes of the borrowers become less compare than the amount which has to pay due to the high rate of interest.
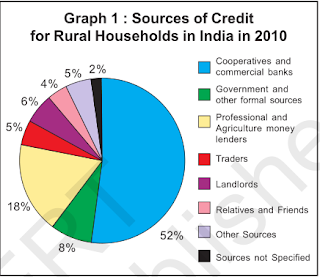
• In this chart, we can see sources of credit in rural areas are mostly dependent on professional and agriculture moneylenders in case of informal sources of loan. For the development of a country, cheap and affordable credit is crucial. Therefore, the government should facilitate formal sources of credit basically in rural areas.
Self-help groups for the poor
• Facilities of banks are not available in all rural areas. So, the poor are dependent on informal sector for borrowing loan. The poor have to pay a high rate of interest to the moneylenders. It is difficult to borrow loan from the bank. Because of the absence of the collateral and documents. And documents and collateral are required for a bank loan. Informal lenders like, moneylenders are often willing to give a loan without collateral because they personally knew the borrowers.
• An organisation constituted to collect the savings of the poor which is known as self-help group. The aim of the organisation is to lend loan at less rate of interest compared to the rate of interest specified by the moneylenders. A self-help group has 15 – 20 members. Savings vary from member to member i.e Rs. 25 to Rs. 100 depending on the ability of the person to save.
• The organisation also provides self-employment opportunity for the member by the way of sanctioning the group. For example, small loans are provided to the members for releasing mortgaged land, for meeting working capital needs, for housing materials, for acquiring assets. There is also a group for repayment of loan. In case of any non-repayment by the one member is followed by the other member of the organisation.
